Model State Validation
BIA Framework offers to you various way to validate your models :
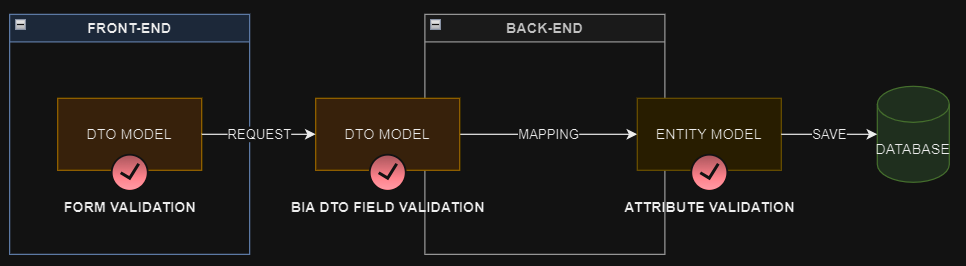
DTO model validation
Front-end
In your DTO model class declaration, you can use Validators in order to constraint user to provide valid data for each fields in a form using your model. Complete the BiaFieldsConfig configuration used to display your model fields into BIA tables with validators :
export class MyClass extends BaseDto {
name: string;
email: string;
export const myClassFieldsConfiguration: BiaFieldsConfig = {
Object.assign(new BiaFieldConfig('name', 'myClass.name'), {
// Field is required and must contains 64 characters max
validators: [Validators.Required, Validators.maxLength(64)]
}),
Object.assign(new BiaFieldConfig('email', 'myClass.email'), {
// Field must be email format
validators: [Validators.email]
}),
}
}
User will not be able to validate the form while the validors requirements are not reached.
See official documentation for more about Validators.
Back-end
In your DTO class, you can use the BiaDtoField attribute to apply validation constraints to each of your fields. You must set the attribute's property EnableModelValidation to true to activate the model validation at field level :
public class MyClassDto : BaseDto<int>
{
[BiaDtoField(EnableModelValidation = true, Required = true, MaxLength = 64)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[BiaDtoField(EnableModelValidation = true, Email = true)]
public string Name { get; set; }
}
Enable this feature on a field will perform a model state validation when a request is received by your endpoint. It will raise into a model state validation error and return to the sender details for each field.
The available validation options into BiaDtoField attribute are listed below :
/// <summary>
/// Indicates whether the property required or not.
/// </summary>
public bool Required { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Set the minimum value of the number property.
/// </summary>
public double RangeMin { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Set the maximum value of the number property.
/// </summary>
public double RangeMax { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Set the minimum length of the string property.
/// </summary>
public int MinLength { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Set the maximum length of the string property.
/// </summary>
public int MaxLength { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Set the regex pattern of the string property.
/// </summary>
public string RegexPattern { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Indicates whether the property is email format or not.
/// </summary>
public bool Email { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Indicates whether the property is phone format or not.
/// </summary>
public bool Phone { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Indicates whether the property is url format or not.
/// </summary>
public bool Url { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Indicates whether the property is credit card format or not.
/// </summary>
public bool CreditCard { get; set; }
Entity model validation
Additionnaly, you can set some ValidationAttribute (official documentation) on your entitiy's fields :
public class MyClass : IEntity<int>
{
[Required]
public int Id { get; set; }
[Required]
[MaxLength(64)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Email]
public string Email { get; set; }
}
By default in BIA Framework, the entity model state validation is disabled.
To turn it on, you must set the corresponding application setting EntityModelStateValidation to true :
{
"EntityModelStateValidation": true
}
The validation will be enable for all the entities with at least one ValidationAttribute on one of their fields. The validation state model will be performed before saving changed entities into database.
NOTE: the entity state model validation will not check the database schema constraints configured by the entity model builder. It will only handle the validation constraints sets by the ValidationAttribute on each entity's fields.